Gas Flow Classification
Order Code: 32371
Category: Thermodynamics Lab
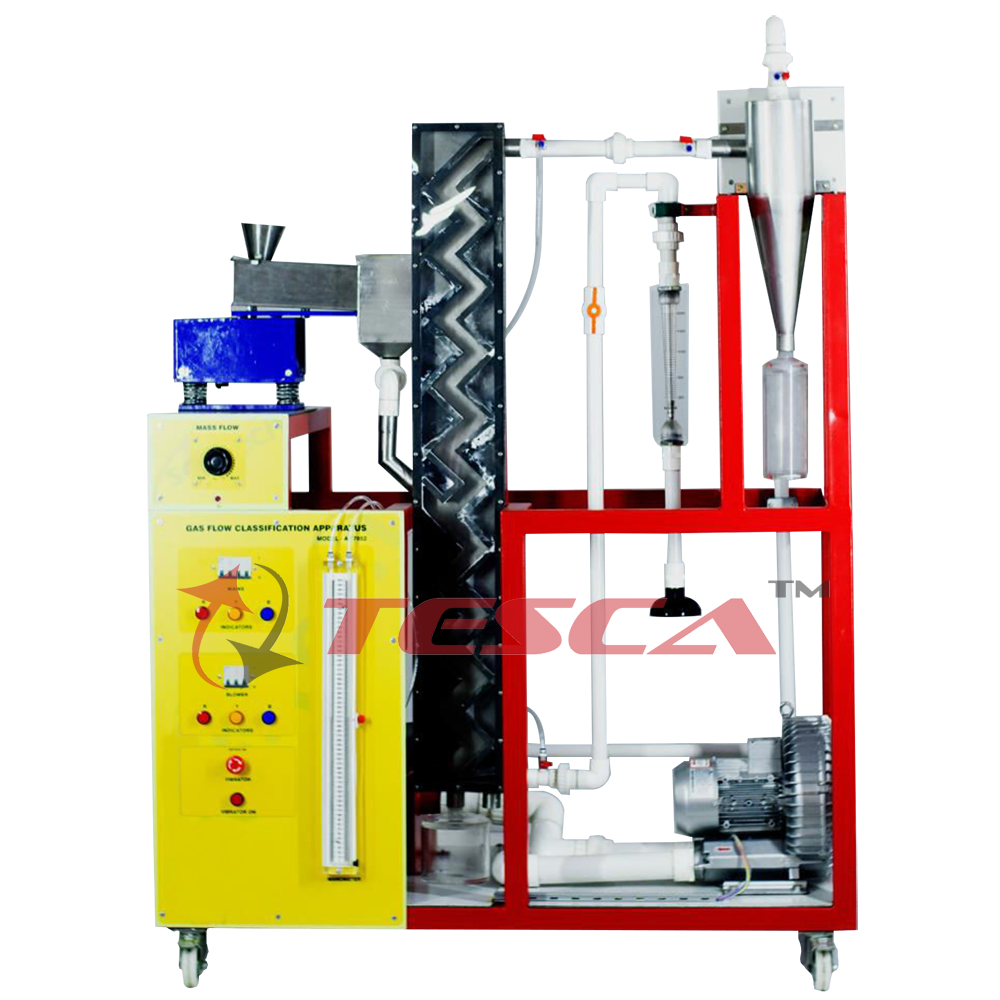
Features Gas flow classification with a zigzag sifter Transparent duct to observe the separation process Practical experiments on a laboratory scale Zigzag sifters permit classification of solid compounds. The solid compound being separated is ...
SPECIFICATION
Features
Gas flow classification with a zigzag sifter
Transparent duct to observe the separation process
Practical experiments on a laboratory scale
Zigzag sifters permit classification of solid compounds. The solid compound being separated is charged into the feed hopper. The compound is fed into the zigzag duct of the sifter at mid-height by way of a vibrating trough. An air flow flows upwards through the vertical duct. Depending on the geometry and density of the particles, they are carried along by the air or drop down due to gravity. At every bend in the duct the solid compound passes through the air flow and falls onto the opposite wall of the sifter. This corresponds to one sifting stage. Owing to the flow conditions, a vortex wake is formed between two bends of the zigzag duct. It ensures that the solid matter moves roughly perpendicular to the air flow. In this way, a transverse sift takes place at every bend. Sequencing of large numbers of such stages results in very fine separation. Tesca Gas Flow Classification 32371 features a 20-stage zigzag duct. Transparent material provides optimum observation of the processes in the duct.
A fan generates the air flow. The volumetric air flow rate and the solid mass flow are adjustable. The fine material transported upwards with the air flow is separated by a cyclone. Pressure measurement points at the relevant positions in the trainer enable the pressure loss to be determined.
Activated carbon in different particle sizes is recommended for use as the feed material. For particle size analyses of the feed and of the coarse and fine material, a balance and a screening machine 32372 are recommended.
Specifications
Zigzag sifter to separate solid compounds
Feed hopper with vibrating trough for feed of solid compound into sifter
Dosage of feed material by way of distance of hopper outlet from vibrating trough and frequency of vibrating trough
Separation of solid compound into coarse and fine material with air flow in 20-stage zigzag duct
Air flow generation by fan; adjustment by valve
Separation of fine material from air flow by gas cyclone with tangential inlet
3 tanks for feed material and coarse and fine materials
Recording of volumetric air flow rate and differential pressure through sifter and cyclone
Technical Specifications
Vibrating trough
Mass flow: max. 10kg/h
Vibration frequency: max. 3000min-1
Zigzag sifter
Height: approx. 1500mm
Cross-sectional area: 40x50mm
Cyclone
Height: approx. 550mm
Diameter: 150mm
Fan
Volumetric flow rate: max. 600m3/h
Power consumption: approx. 3600W
Tanks
Feed hopper: 3L
Coarse material: 2L
Fine material: 2L
Measuring ranges
Cyclone and sifter differential pressures: 0…100mbar
Volumetric flow rate (air): approx. 10…100m3/h
Experiments
Learning the fundamental principle of wind sifting (gas flow classification)
Sorting
Coarse material fraction
Fine material fraction
Dependent on solid mass flow rate and volumetric air flow rate
Classifying 32372
Fraction balance
Separation function
Separation size
Sharpness of separation
Dependent on solid mass flow rate and volumetric air flow rate
Pressure losses of
Sifter
Cyclone
Dependent on solid mass flow rate and volumetric air flow rate
Requirements
Water connection 300L/h, drain
Mains Power 220 – 240V @ 50Hz, 1Ph










 91-9829132777
91-9829132777