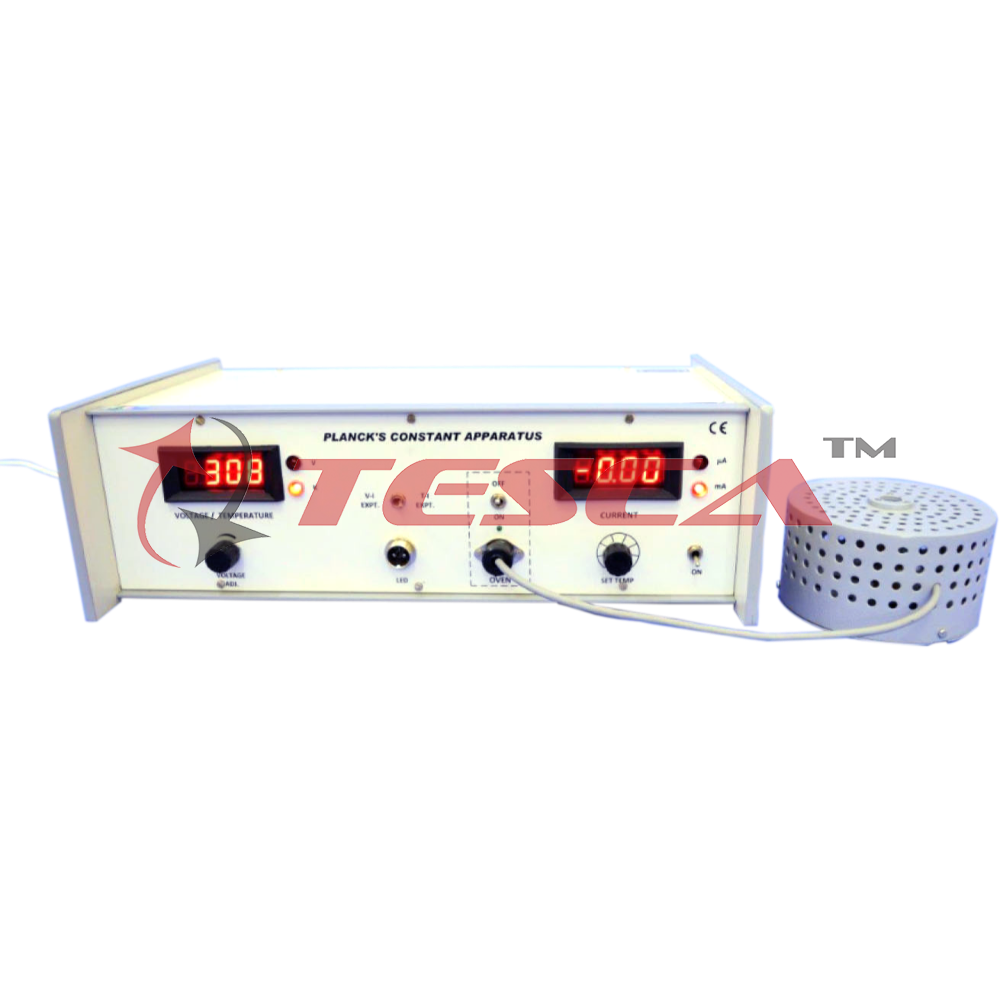
Determination of Planck Constant by means of LED

Order Code: 55529
Category: Physics Trainers
• Highly accurate results • Precise measurement of Band-Gap • Clear physical interpretation • Self contained unit with no extra accessory required Several proposals to measure the Planck's Constant for dida...
SPECIFICATION
• Highly accurate results
• Precise measurement of Band-Gap
• Clear physical interpretation
• Self contained unit with no extra accessory required
Several proposals to measure the Planck's Constant for didactical purposes, using the current - voltage (I-V) characteristics of a light emitting diode (LED) have been made quite regularly in the last few years. The reason is that the experiment can be done easily in any lab and the result are surprisingly good ( 10%). The physical interpretation however is not completely clear and this has raised many discussions, which has been published almost with same regularityasthe proposals themselves.The present experiment is based on diode current for V<V0, using the diode law.
l = Io exp [- e (V0- V)/hkT]
where, e is electronic charge, k is Boltzmann constant, T is absolute temperature and i is material constant which depends on the type of diode, the location of recombination region, etc.
The correct method to determine the real height oi the potential energy barrier V. is to directly measure the dependence oi the current on temperature keeping the applied voltage V slightly below V0. The idea is that the disturbance to Vo is as little as possible. The slope of In I vs. 1/T curve gives e (Vo - V)hk (Fig. 1). The constant v is determined from I-V characteristics oi the diode (Fig. 2) at room temperature from the relation
h= (e/kt) (DV/DIn I)
Compared with previous methods, this determination of V. is more precise and more accurate and at the same time the physical interpretation is more transparent.
The Planck's constant is then obtained by the relation
h = e Vo l/c
The wavelength (X) of the light emitted by the diode can be measured by a transmission grating spectrometer normally available in the lab. The value of Planck's constant obtained from this method is within 5% of accepted value (6.62x10-34J oules.sec)










 91-9829132777
91-9829132777