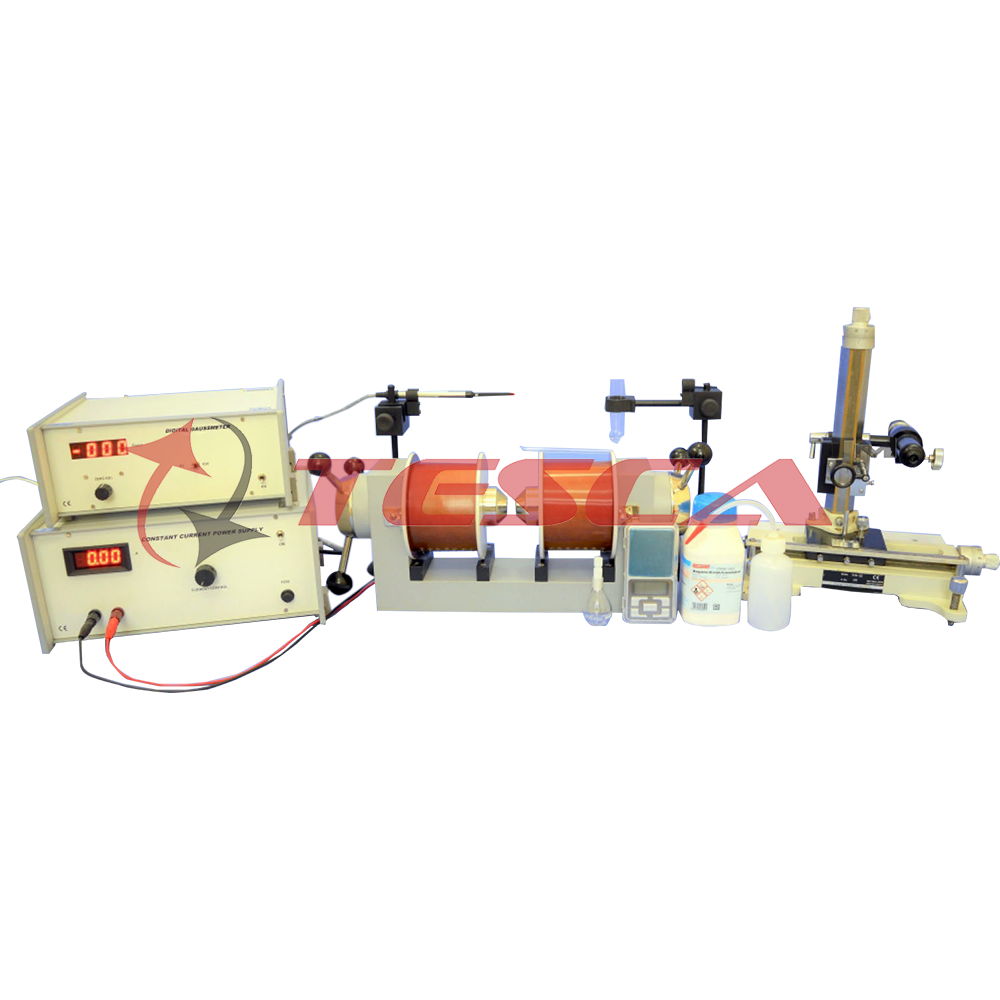
Apparatus for the Measurement of Susceptibility of Paramagnetic Solution by Quinck's Tube Method
Order Code: 55538
Category: Physics Trainers
It was established by Faraday in 1845 that magnetism is universal property of every substance. He classified all magnetic substances into two classes, viz., paramagnetic and diamagnetic. Weber, later on, tried to explain para and diamagnetic pro...
SPECIFICATION
It was established by Faraday in 1845 that magnetism is universal property of every substance. He classified all magnetic substances into two classes, viz., paramagnetic and diamagnetic. Weber, later on, tried to explain para and diamagnetic properties on the basis of molecular currents. The molecular current gives rise to the intrinsic magnetic moment to the molecule, and such substances are attracted in a magnetic field, and called paramagnetics. The repulsion of diamagnetics is assigned to the induced molecular current and its respective reverse magnetic moment. The force acting on a substance, either of repulsion or attraction, can be measured with the help of an accurate balance in case of solids or with the measurement of rise in level in narrow capillary in case of liquids. The force depends on the susceptibility K, of the material, i.e., on ratio of intensity of magnetisation to magnetising field (I/H). Evidently it refers to that quantity of substance by virtue of which bodies get magnetised. Quantitatively it refers to the extent of induced magnetisation in unit field. If the force on the substance and field are measured, the value of susceptibility can be calculated. The value of the susceptibility K of liquid aqueous solution of a paramagnetic substance in air is given by a well know expression:
- Quinck’s tube with stand
- Sample: MnS042H20H2
- Digital Balance 500gms (LC:0.1gm)
- RD Bottle
- Mixing Bottle
- Electromagnet
- Constant Current Power Supply
- Digital Gaussmeter
- Travelling Microscope
- Travelling Microscope
- (Horizontal and Vertical)
- True achromatic objective with 7.5cm focussing distance
- 10X Ramsden eyepiece with fine cross wire
- Horizontal scale: 20cm divided at 0.5mm interval
- Vertical scale: 15cm divided at 0.5mm interval
- Venier scales: 50 divisions with a least count of 0.01mm









 91-9829132777
91-9829132777