Three Hinged Arch

Order Code: 32165
Category: Strength of Materials Lab
Statically determinate three-hinged arch Symmetrical or unsymmetrical arch Various load cases: point load, distributed load, moving load Bridges are often constructed as three-hinged arches. This type of construction is particularly suitable when ...
SPECIFICATION
Statically determinate three-hinged arch
Symmetrical or unsymmetrical arch
Various load cases: point load, distributed load, moving load
Bridges are often constructed as three-hinged arches. This type of construction is particularly suitable when compression-proof building materials are available. Horizontal thrust occurs in the arch at the supports. It permits much lower bending moments in the arch than in the case of a beam on two supports with the same span. A significant longitudinal compressive force is active in the arch to produce this effect.
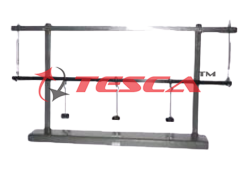
A three-hinged arch consists of a curved beam mounted on two fixed supports, and usually featuring the so-called crown hinge at its crown. The hinges on the two fixed supports absorb vertical and horizontal forces, and are known as abutment hinges. Their connecting line is the springing line. The crown hinge renders the system statically determinate.
Tesca Three Hinged Arch includes two long arch segments and one short segment, of which two at a time are connected by a hinged joint producing a symmetrical or unsymmetrical three-hinged arch. The arch under investigation can be subjected to point, distributed or moving load. Weight sets compensate for the support reactions of a abutment hinge, so enabling a comparison between calculated and actual measured values.
All the component elements of the experiment are clearly laid-out and housed securely in a storage system. The complete experimental set-up is arranged in the frame.
The well-structured instructional material sets out the fundamentals and provides a step-by- step guide through the experiments.
Specifications
Investigation of 2 statically determinate three-hinged arches
3 arch segments: 2x long (together making a symmetrical arch), 1x short (together with 1x long: unsymmetrica larch)
Hinged arch with 3 hinges: 1 crown hinge, 2 abutment hinges at the bearing points
Arch subjected to point load, distributed load (each by weights) or moving load
4 sets of weights to compensate for the support reactions of an abutment hinge
Storage system to house the components
Experimental set-up in frame
Technical Specifications
Aluminum arches
2x long: 480mm, total arch length: 960mm
1x short: 230mm, total arch length: 710mm
Arch height: 250mm
Weights
4x 1N (hangers)
- 36x 1N
- 16x 5N
Experiment Possibilities
Familiarization with three-hinged arches (unsymmetrical and symmetrical)
Application of the method of sections and the conditions of equilibrium to calculate the bearing forces for
Point load, distributed load, moving load
Investigation of the influence of the load on the horizontal thrust in the supports
Determination of the lines of influence for the supports under a moving load
Comparison of the calculated and measured support reactions for static and moving load
Scope of Delivery
Ÿ 3 arch segments Ÿ 1 moving load
2 bearings
4 sets of weights with deflection rollers
1 storage system with foam inlay
1 set of instructional material










 91-9829132777
91-9829132777