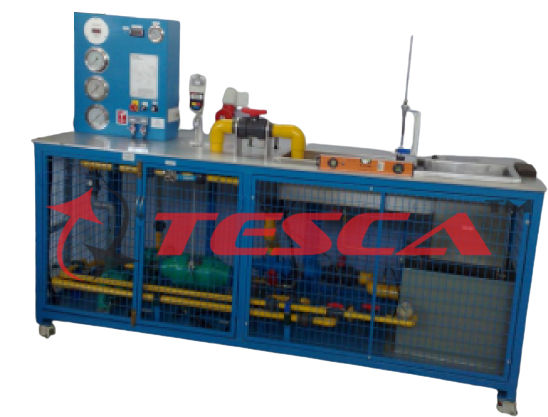
Pumps Comparison Apparatus
Order Code: 32092
Category: Fluid Mechanics Lab
Features: Investigation of the operating behavior of centrifugal, piston, and side-channel pumps1 All pumps driven separately by three- phase AC motors1 Centrifugal pumps can be operated in series or parallel The experiments familiarize student...
SPECIFICATION
Features:
Investigation of the operating behavior of centrifugal, piston, and side-channel pumps1
All pumps driven separately by three- phase AC motors1
Centrifugal pumps can be operated in series or parallel
The experiments familiarize students with various pump types, such as centrifugal and positive displacement pumps.
Tesca Pumps Comparison Apparatus includes two centrifugal pumps, one piston pump as a positive-displacement pump, and a self-priming side-channel pump. The side-channel pump works primarily as a centrifugal pump and, depending on the liquid level, can also act as a positive displacement pump. This means, as a special feature, the side-channel pump also permits gases to be pumped.
The pump being investigated pumps water in a closed circuit. In the process, the performance data of the pump and pressure losses in the pipeline are recorded. The centrifugal pumps can also be operated in parallel or in series. Each pump is driven by a separate three-phase AC motor. The speed of the motors for the centrifugal pumps is variably adjustable by a frequency converter. All motors are mounted on swivel bearings, so the torque can be measured by way of a force sensor, enabling the mechanical drive power output to be determined.
One free position is likewise equipped with a reversible three-phase AC motor with variable speed.
This position can be used for mounting any pump.
Experiments demonstrate the basic operating behavior of various pump types.
Relevant measured values can be read on digital displays. At the same time, the measured values can also be transmitted directly to a PC via USB. The data acquisition software is included. The performance data of the pump and losses in the pipeline are calculated by the software and represented by characteristic curves. The operating point of the pump can be determined from these characteristics.
The well-structured instructional material sets out the fundamentals and provides a step-by-step guide through the experiments.
Specifications:
Experiments relating to key issues in pump engineering
Comparison of various pump types: centrifugal pump, piston pump, side- channel pump
Operation of centrifugal pumps in parallel or series
Free position for additional pump
Three - phase AC motors for centrifugal pumps and additional motor with variable speed by frequency converter
Optional software for data acquisition via USB under Windows Vista or Windows 7
Technical Specifications:
Centrifugal pump 2x
Max. flow rate (Q): 300L/min
Max. head (H): 16,9m
Nominal speed: 2900min-1
Three-phase AC motor 2x, for centrifugal pump
Power output: 750W
Speed range: 750...3000min-1 Side-channel pump, self-priming, one- stage
- Q: 83,3L/min, H: 50m
Nominal speed: 1450min-1
Three-phase AC motor for side-channel pump
Power output: 1,1kW
Speed: 1500min-1 Piston pump
- Q: 17L/min, H: 60m
Nominal speed: 405min-1
Three-phase AC motor for piston pump
Power output: 0,55kW
Speed: 1500min-1
Three-phase AC motor, additional motor, reversible
Power output: 0,75kW
Speed range: 750...3000min-1 Measuring ranges
Flow rate: 0...500L/min
Intake pressure: -1...1,5bar
Delivery pressure: 0...10bar
Torque: 0...15Nm
- Speed: 0...3000min-1
Pump electrical power consumption: 0...2000W
Experiments:
1. Investigation and comparison of the operating behavior of various pump types:
> Centrifugal pumps
> Piston pump (positive - displacement pump)
> Side-channel pump
2. Plotting a pump characteristic curve
3. Plotting a system characteristic curve
4. Determining efficiency
5. Investigation and comparison of parallel and series configuration of centrifugal pumps - comparison of pump types
Requirements:
400V, 50/60Hz, 3 phases or 230V, 60Hz, 3 phases








 91-9829132777
91-9829132777