Precipitation and Flocculation Apparatus

Order Code: 32117
Category: Fluid Mechanics Lab
Features: Removal of dissolved substances (e.g. iron) by precipitation and flocculation Sedimentation of the flocs in the lamella separator Tesca Precipitation and Flocculation Apparatus demonstrate the removal of dissolved ...
SPECIFICATION
Features:
- Removal of dissolved substances (e.g. iron) by precipitation and flocculation
- Sedimentation of the flocs in the lamella separator
Tesca Precipitation and Flocculation Apparatus demonstrate the removal of dissolved substances by precipitation and flocculation with subsequent sedimentation.
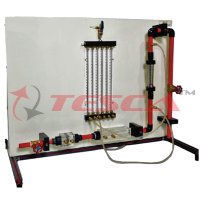
First, raw water is produced in a tank to contain dissolved metal (e.g. iron). A pump transports the raw water to the precipitation tank. Here the precipitant is added (e.g. caustic soda). Due to the reaction of the dissolved metal ions with the precipitant, insoluble metal hydroxides form (solids). From here the water flows into a flocculation tank divided into three chambers. The purpose of flocculation is to improve the sedimentation properties of the solids. By adding a coagulant in the first chamber the repulsive forces between the solid particles are canceled out. The solid particles aggregate into flocs (coagulation). To generate larger flocs, a flocculant is then added (flocculation). In the third chamber, low flow velocities are present to prevent any turbulence. Turbulence would impede the formation of flocs. The now well sedimentable flocs are then separated from the treated water in a lamella separator. The treated water and the sedimented flocs (sludge) are collected in two tanks.
Flow rate, temperature, and pH value are measured. In addition, the pH value in the precipitation tank can be controlled. For measuring the conductivity an external meter is available. Samples can be taken at all relevant points.
Analysis technology is required to analyze the experiments. The choice of analysis technology depends on the substances used. Trivalent metallic salts are usually well suited as coagulants. Common flocculants are organic polymers.
Specifications:
- Precipitation and flocculation of dissolved substances (e.g. iron)
- Separate supply unit with tank and pump for raw water
- Precipitation tank with stirring machine
- Flocculation tank with 3 chambers and 4 stirring machines
- 3 metering pumps for chemicals
- Sedimentation of the flocs in the lamella separator
- Measurement of flow rate, temperature, and pH value
- Control of the pH value
Technical Specifications:
Tanks
Raw water and treated water: each 300L
Precipitation tank: 10L
Flocculation tank: 45L
Sludge tank: 15L
Lamella separator
Number of lamellas: 6
The angle of inclination of lamellas: 60°
Raw water pump
Max. flow rate: 180L/h
Max. head: 10m
Metering pumps
Max. flow rate: each 2,1L/h
Max. head: each 160m
Stirring machines
Max speed: each 600min-1
Measuring ranges
Flow rate: 15…160L/h
pH value: 0…14
Temperature: 0…60°C
Conductivity: 0…2000µS/cm
Experiments:
- Familiarization with precipitation and flocculation
- Effect of the pH value on precipitation
- Creation of a stable operating state
- Determination of the required metering quantities (precipitant, coagulant, flocculant)
- Functional principle of a lamella separator
Requirements:
Mains Power 220 – 240V @ 50Hz, 1Ph








 91-9829132777
91-9829132777