Parabolic Arch

Order Code: 32168
Category: Strength of Materials Lab
Features Statically determinate or statically indeterminate parabolic arch under load Deformations of the arch under load Support reactions of the arch Parabolic arches are popular elements in construction engineering. They can be ...
SPECIFICATION
Features
Statically determinate or statically indeterminate parabolic arch under load
Deformations of the arch under load
Support reactions of the arch
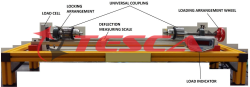
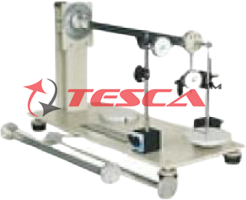
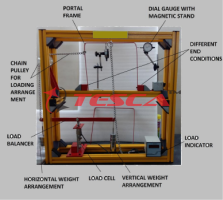
Parabolic arches are popular elements in construction engineering. They can be employed as bridges or beams for example. Normally these bridges are statically indeterminate. The special feature of the parabolic arch is that in the arch only normal forces and bending moments occur, but no shear forces. That is the case when the arch is subjected to a uniform distributed load and both ends are mounted in fixed bearings. This enables arches to be constructed from loosely set stones – a construction technique which has been in existence for many centuries. Loads acting upon the inner of the arch are primarily compressive forces in the direction of the normal force at every point of the arch. Tesca Parabolic Arch includes a pre-shaped parabolic arch. It can be subjected to point or distributed loads. One of the arch’s supports is fixed, the other is on a roller bearing. Weight sets are used to cancel this movement. The movable support thus becomes a fixed support. Additional weight sets compensate for the vertical support reaction.
Dial gauges record the deflection of the arch under load and the horizontal displacement of the movable bearing. As long as the roller bearing is movable, the arch is statically determinate, though it is substantially deformed under load. As soon as the roller bearing becomes immovable, the arch is no longer statically determinate and is deformed only to a minor degree.
All the component elements of the experiment are clearly laid-out and housed securely in a storage system.
The complete experimental set-up is arranged in the frame .
The well-structured instructional material sets out the fundamentals and provides a step-by- step guide through the experiments.
Specifications
Investigation of a parabolic arch, optionally statically determinate (1 fixed support, 1 movable support) or indeterminate (2 fixed supports)
Loading of the arch with a distributed load by way of 7 evenly distributed weights or by point loads
Dial gauges record the deformation of the arch under load
4 sets of weights to compensate for the reactions of a fixed support
Storage system to house the components
Experimental set-up in frame
Technical Specifications
Parabolically pre-shaped steel arch
Length: 960mm
Height: 262mm
Cross-section: 20x6mm
Dial gauges
Measuring range: 0...25mm, graduations: 0,01mm
Weights
11x 1N (7+4 hangers)
- 16x 1N
- 19x 5N
Experiment Possibilities
Mechanical principles of the parabolic arch
Differences between statically determinate and statically indeterminate arches
Measurement of the deformations of the arch under load
Measurement of the support reactions on the statically indeterminate arch under load
Calculation of the support reactions
Influence of point load or distributed load on reaction forces and deformation of the arch
Scope of Delivery
1 arch with 7 shackles + 7 weight hangers
4 sets of weights
2 deflection rollers with fixture
1 bearing
2 dial gauges
1 storage system with foam inlay
1 set of instructional material








 91-9829132777
91-9829132777