Fluidized Bed Formation

Order Code: 32115
Category: Fluid Mechanics Lab
Features: Experimental investigation of the fluidization process Comparison of fluidized bed formation in gases and liquids Pressure loss in fixed beds and fluidized beds Optimum observation of processes through...
SPECIFICATION
Features:
- Experimental investigation of the fluidization process
- Comparison of fluidized bed formation in gases and liquids
- Pressure loss in fixed beds and fluidized beds
- Optimum observation of processes through transparent tanks
Bulk solids can be transformed from a fixed bed into a fluidized bed when liquids or gases pass through them. The areas of application of fluidized beds include the drying of solids and a wide variety of chemical processes.
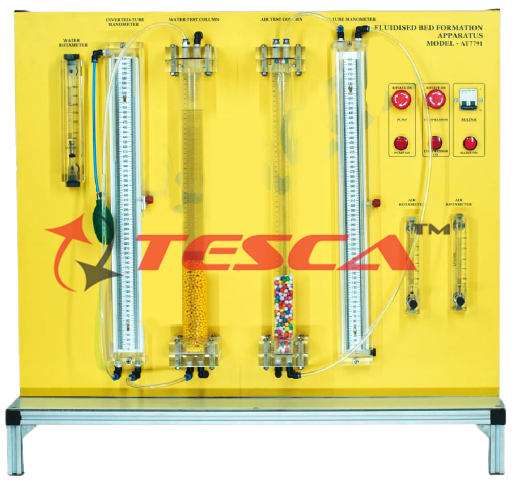
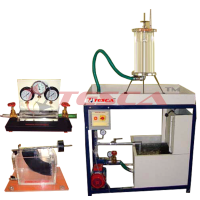
Tesca Fluidized Bed Formation Apparatus features two transparent test tanks for fluidized bed formation in water and air. A diaphragm pump delivers water from a storage tank into the bottom of the left side test tank. The water flows upwards through a porous sintered-metal plate. On the sintered-metal plate is a bulk solid. If the velocity of the water is less than the so-called fluidization velocity, the flow merely passes through the fixed bed. At higher velocities, the bed is loosened to such an extent that individual solid particles are suspended by the fluid. If the velocity is increased further, particles are carried out of the fluidized bed. A filter at the top of the test tank holds these particles back. The water flows back into the storage tank.
The right-side test tank is similar in construction to the left-side one. An airflow generated by a compressor flows through it.
Manometers are mounted on both test tanks to measure the pressure loss. The flow rates are adjusted by way of valves and can be read from flow meters. The test tanks are removable. This makes it easy to change the bulk solid filling.
Glass-shot beads in a range of particle sizes are provided as the bulk solid filling.
Specifications:
- Investigation of fluidized bed formation of solids in air and water
- 2 transparent test tanks to observe fluidized bed formation in air/water
- 1 manometer per tank to measure the pressure loss through each test tank
- 1 steel rule per tank to measure the change in height of the fluidized beds
- Both test tanks removable for filling
- Storage tank with diaphragm pump for water supply
- Diaphragm compressor with compressed air accumulator for compressed air supply
- Adjustment of flow rate for both media by valves and flow meter
Technical Specifications:
2 test tanks
Length: 550mm
Inside diameter: 44mm
Scale division: 1mm
Material: PMMA
Diaphragm pump (water)
Max. flow rate: 1,7L/min
Max. head: 70m
Diaphragm compressor (air)
Max. volumetric flow rate: 39L/min
Max. pressure: 2bar
Tanks
Water storage tank: approx. 4L
Compressed air accumulator: 2L
Measuring ranges
Pressure (water): 0…500mmWC
Pressure (air): 0…200mmWC
Flow rate (water): 0,2…2,2L/min
Flow rate (air): 4…32L/min
Experiments:
- Fundamentals of the fluidization of bulk solids
- Observation and comparison of the fluidization process in water and air
- Pressure loss depends on the flow velocity
- Pressure loss depends on the type and particle size of the bulk solid
- Determination of the fluidization velocity and comparison with theoretically calculated values (Ergun equation)
- The dependency of the height of the fluidized bed on the flow velocity
- Verification of Carman-Kozeny equation
Requirements:
Mains Power 220 – 240V @ 50Hz, 1Ph








 91-9829132777
91-9829132777