Deformation of Trusses
Order Code: 32155
Category: Strength of Materials Lab
Features Elastic deformation in a single plane truss Construction of various truss forms Application of Castigliano’s first theorem When a component is placed under load it undergoes elastic deformatio...
SPECIFICATION
Features
- Elastic deformation in a single plane truss
- Construction of various truss forms
- Application of Castigliano’s first theorem
When a component is placed under load it undergoes elastic deformation. This deformation can be calculated by determining elastic lines for example. Elastic lines describe the deformation of the complete component in the form of a mathematical equation. In reality, it is often only the deformation at specific points on the component which is of interest. Energy methods can be applied to determine these deformations more simply. Castigliano’s first theorem uses energy methods to calculate the deformation of a point on the component. The theorem is applicable to both statically determinate and indeterminate systems.
Specifications
Investigation of the deformation of statically determinate trusses
Construction of different truss forms possible
2 supports with node discs
Load application device with force measurement dial gauge mountable on different node discs
Dial gauge to record the deformation of the truss under load
Cross arm for lateral stability of truss
Storage system to house the components
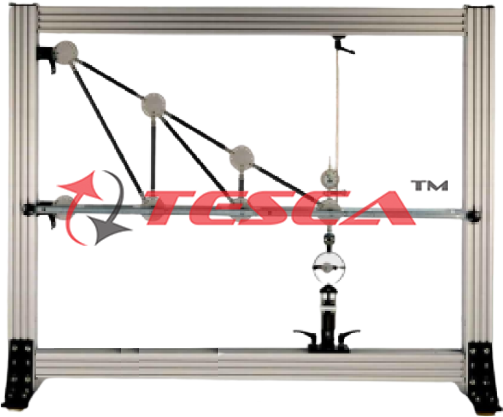
Tesca Deformation of Trusses, the deformation of a single plane truss at one point is determined using Castigliano’s first theorem. The truss under investigation is made of bars joined together by an articulated construction using node discs. The trusses can be considered ideal trusses. The bars have special snap-lock fixtures on their ends allowing them to be fixed easily into the node discs. A load application device attached to a node disc generates an external force. The range of different bar lengths provided permits three forms of truss to be constructed. The bars are made of PVC, so their deformations are clearly visible.
The well-structured instructional material sets out the fundamentals and provides a step-by-step guide through the experiments.
Technical Specifications
Truss with 19 PVC bars
- Height of truss max. 450mm
- Length of truss max. 900mm
- Bar lengths
? 2x 150mm
? 5x 259mm
? 7x 300mm
? 1x 397mm
? 3x 424mm
? 1x 520mm
- Angle between bars: 30°, 45°, 60°, 90°
- Maximum bar force: 200N Load application device
- Measuring range: -500...+500N, graduations: 10N Dial gauge
- Measuring range: 0...0,10mm, graduations: 0,01mm
Experiments
- Elastic deformation of the truss under point load
- Calculation of support reaction and bar forces
- The principle of work and strain energy
- Application of Castigliano’s first theorem to calculate the deformation at a defined point
- Verification of the calculated deformation possible by the principle of virtual work
- Comparison of the deformations of different trusses under the same load
- Comparison of measured and calculated deformation
Scope of Delivery
- 1 set of bars
- 5 node discs
- 2 supports with node disc
- 1 load application device
- 1 dial gauge with bracket
- 1 storage system with foam inlay
- 1 set of instructional material










 91-9829132777
91-9829132777