Bio Ethanol Plant

Order Code: 32499
Category: Other Trainers
Features Practical process for production of ethanol from starch-based biological raw materials System control using a PLC, touch screen for display and operation PC aided data acquisition via USB interface In many the chemical and foodstuffs ind...
SPECIFICATION
Features
Practical process for production of ethanol from starch-based biological raw materials
System control using a PLC, touch screen for display and operation
PC aided data acquisition via USB interface
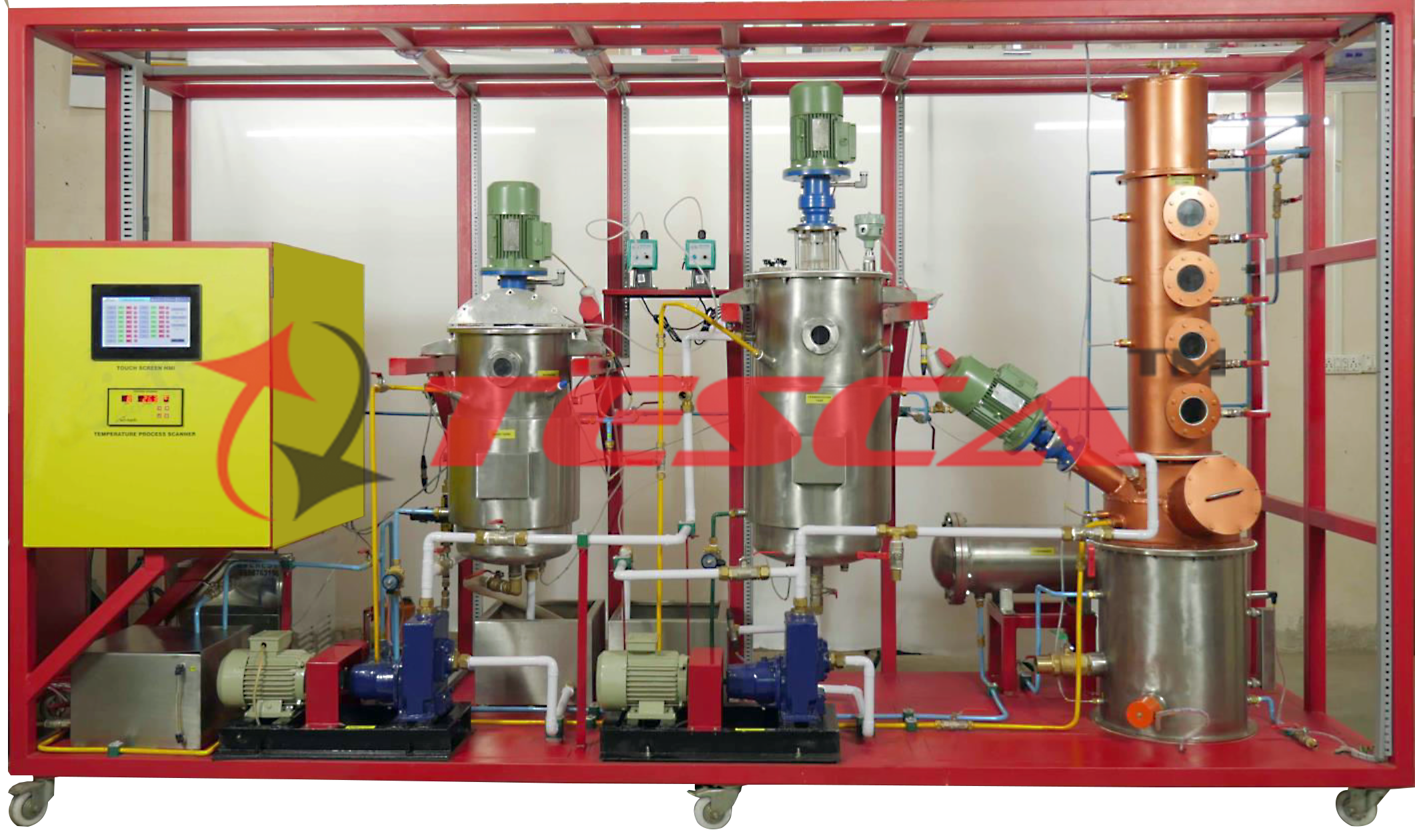
In many the chemical and foodstuffs industries, ethanol (alcohol) is increasingly used as a fuel. Bio Ethanol Plant Order Code : 32499 can be used to conduct realistic experiments for the production of ethanol from starch-based raw materials such as potatoes. The experimental plant consists of three main components: a mash tank, a fermentation tank and a distillation unit. A mixture of water, finely chopped potatoes and alpha-amylase (enzyme) is filled into the mash tank. To dissolve the tightly packed starch chains in the potatoes, heating steam is injected into the mixture via a nozzle (gelatinisation). This increases the flow resistance of the mash, which would prevent further processes. The alpha-amylase breaks up the starch chains (liquefying) thereby reducing the flow resistance. Gluco-amylase is used to convert the starch into sugar (saccharification). This enzyme requires lower temperatures and pH values. The temperature is reduced using the water cooling jacket around the mash tank, the pH value is adjusted by the addition of acid and caustic. After saccharification the mash is pumped into the fermentation tank. During the fermentation process in this tank, ethanol is produced. A water cooling system controls the temperature. After the fermentation process, the mash is pumped into the distillation unit. This is equipped with a bubble cap tray column for separation of the ethanol. Two tanks are available, one for the spent mash, the other for the distilled ethanol. The experimental plant has comprehensive measurement, control and operating functions, which are controlled via a PLC or DAQ. An optional touch screen displays measured values and permits the operation of the system.
Specifications
Batch conversion of starch-based raw materials into ethanol
Open mash tank with water-jacket cooling, steam injection and stirrer
Closed fermentation tank with stirrer and water-jacket cooling/heating
Distillation unit with 3 bubble cap trays, dephlegmator, condenser and stirrer
2 pumps for delivering the mash pH value control in the mash tank with acid and caustic delivered by metering pumps
Adjustment of the amount of injected heating steam, the cooling water flow rates and the head temperature by PLC Control Panel
Distillation: separation of ethanol from the mash means of PID / DAQ controllers
System control using a PLC or DAQ; operated by optional touch screen
Sci-tech software for data acquisition via USB under Windows 7, 8.1, 10
Technical Specifications
Mash tank: 40L
Fermentation tank: 50L
Product tank: 10L
Spent mash: 30L
Distillation unit
column: DxH: 220x1200mm
sump capacity: 45L
sump heater: 0…7500W
Air-operated diaphragm pumps
Drive pressure: 2bar
max. flow rate: 15L/min
max. head: 20m
max. solid lump size: 4mm
metering pumps (acid and caustic)
max. flow rate: each 2,1L/h
Measuring ranges
temperature: 10x 0…150°C
water quantity mash tank: 0…20L
pH value: 2…10
pressure heating steam: 0…10bar
Experiments
Familiarization with the necessary individual steps and system components for production of ethanol:
Gelatinisation by steam injection
Liquefaction by use of alpha-amylase
Saccharification by use of gluco-amylase
Fermentation: conversion of sugar into ethanol by yeast cultures under anaerobic conditions
Requirements
Ÿ Mains Power 220 – 240V @ 50Hz, 1Ph & 400 – 440V @ 50Hz, 3Ph










 91-9829132777
91-9829132777