Table of Contents
What is an Alternating Current?
The alternating current is the normal type of electrical force created and disseminated due to its simplicity of generation and circulation. The substituting voltage is handily moved forward and down to suit any necessary voltage level.
the electrical power is communicated at high voltages and low flows to limit power misfortunes in the conductor. It is subsequently ventured down at the conveyance and shopper level to suit the buyer’s necessities.
Larger electrical and electronic hardware parts use AC power at either 220-240 volts or 110-120V for homegrown and office applications and 415V for mechanical.
Types of AC Power Distribution:
AC distribution systems are of the following types:
- Single-phase, 2-wire system
- Single-phase, 3-wire system
- Two-phase, 3-wire system
- Two-phase 4-wire system
- Three-phase 3-wire system
- Three-phase, 4-wire system
1. Single Phase, 2-Wire Distribution:
The 2 wire single phase AC distribution is used for extremely low distances. A single-phase has a two-wire system where one of the wires is earthed.
2. Single Phase, 3-Wire System:
This system has a 3-wire dc distribution system. The nonpartisan wire is tapped from the auxiliary twisting of the transformer and earthed. This framework is likewise called a parted phase power conveyance system.
3. Two-Phase, 3-Wire System:
In a two-phase system, the fourth wire is taken from the intersection whose voltage is in quadrature with the other two-phase windings. The voltage between the impartial wire and both of the external stage wires is V.
While the voltage between external stages wires is √2V. When contrasted with a two-stage 4-wire framework, this framework experiences voltage irregularity because of unsymmetrical voltage in the nonpartisan.
4. Two-Phase, 4-Wire System:
The four wires are taken from two-phase windings in this phase whose voltages are quadrature. The mid-point of both stage windings are associated together.
If the voltage is of the same phase between two wires, i.e., V, then the voltage would be 0.707V between two wires.
5. Three Phase, 3-Wire Distribution System:
3 phase wire system is used for AC power conveyance. The three phases might be delta associated or star associated with star point generally grounded.
6. Three Phase, 4-Wire Distribution System:
A star phase winding is used in this wiring system, and the 4th wire is taken from the start point. Let’s say the voltage of each winding is V, then the line-to-impartial voltage would be V, and the line-to-line voltage would be √3V.
Types of AC Distribution System:
AC Distribution System:
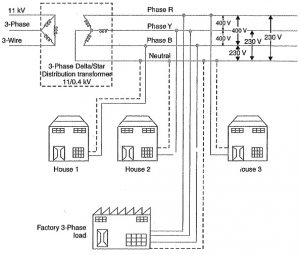
Image Credit: EEEGuide.com
Nowadays, electrical energy is created, sent, and distributed through a rotating flow.
One significant justification of the broad utilization of rotating current in inclination to coordinate current is the way that exchanging voltage can be advantageously changed in extent through a transformer.
A transformer has made it easy to communicate ac power, it can be used at high voltage with protected potential. High transmission voltages have reduced the current flow in conductors, which leads to fewer misfortunes.
There is no positive line among transmission and dispersion as indicated by voltage or mass limit.
Be that as it may, as a general rule, the AC Distribution System is the electrical framework between the progression down substation taken care of by the transmission framework and the shoppers’ meters. It is further classified into-
1. Primary Distribution System:
It is that piece of AC Distribution System that works at voltages fairly higher than general usage. It handles enormous squares of electrical energy than the normal low-voltage purchaser employments.
The voltage utilized for essential circulation relies on the ability to be passed on and the distance of the substation needed to be taken care of. The most usually utilized essential dissemination voltages are 11 kV, 6.6 kV, and 3.3 kV. Because of monetary contemplations, essential dissemination is done by a 3-stage, 3-wire framework.
2. Secondary Distribution System:
Secondary AC distribution systems include the range of voltages in which buyers use electrical energy. The auxiliary circulation utilizes a 400/230 V, 3-stage, 4-wire framework.
Also want to know about DC Power? Read Here: DC Power System & Working.
Function of the AC Power Supply:
The fundamental function of an AC power supply is to change the rotating flow (AC) into a stable direct flow (DC) voltage, which would then be able to be utilized to control diverse electrical gadgets. Rotating flow is utilized for shipping electric force the whole way across the electric matrix, from generators to end clients.
How AC Power Supplies Works?
The power supply is utilized to lessen the mains power at 240 volts AC down to something more helpful, say 12 volts DC. There are two sorts of force supply, straight and switch mode. A straight force supply utilizes a transformer to decrease the voltage.
The proportion of essential windings (associated with the mains) to the number of optional windings (associated with the yield) would give the proportion of how much the voltage decreased by, for this situation, a proportion of 20:1 lessens the 240 volts AC input into 12 volts AC on the auxiliary windings.
A switch-mode supply works to reduce the voltage by turning its main power. For this situation, the decrease in voltage relies on the proportion of the on and off time. Exchanging happens exceptionally quick, at 10,000 times each second or speedier. Utilizing this strategy, the massive transformer found in a direct inventory can be supplanted with a more modest one.
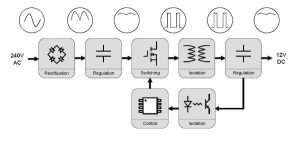
Image Credit: Kitronik.co.uk
The AC signal is managed to deliver a high DC voltage. This is then turned on and off quickly by a FET. Then, at that point, the exchanged sign goes through a transformer; albeit this can decrease the voltage, it secludes the yield from the mains power (for security reasons).
The yield input is then used to control the imprint space proportion of the exchanging, so the yield stays at the necessary voltage. The transformer utilized in a switch mode supply is a lot more modest and less expensive than the kind utilized in straight stock; however, it should have the option to deal with the higher exchanging frequencies.
Advantages of AC Transmission:
- It requires just two conductors.
- There is no issue of capacitance and phase uprooting in AC transmission.
- The voltage drop in DC transmission lines is not similar to AC transmission for a similar end voltage.
- As there is no skin impact on conductors, subsequently, the whole cross-segment of the conductor is conveniently used along these lines influencing saving in material.
- A similar value of voltage protecting materials on dc lines experiences less pressure when contrasted with those on ac transmission lines.
- A DC line has less crown misfortune and decreased impedance with correspondence circuits.
- There is no issue of system shakiness, so normal in ac transmission.
Disadvantages of AC Transmission:
-
- Generation of power at high dc voltages is troublesome because of recompense issues and can’t be helpfully used at Consumer closes.
- Move forward or venture down change of dc voltages is beyond the imagination in gear like transformer.
Tesca Global is the leading manufacturers and exporter of AC, DC systems. Want to get your hands on AC systems? Get in touch with us today!





Add comment